Clamp ground resistance meter is to quickly measure the resistance value between the equipment and the earth without disconnecting the ground down conductor and auxiliary electrode under the condition of multi-point grounding. The maximum measurement range of ground resistance is 1000Ω, and the minimum resolution is 0.001Ω. According to the situation and selection specifications, the clamp ground resistance meter can also measure the current, leakage current and neutral current, and is widely used in the ground resistance measurement of electric power, telecommunications, meteorology, oil fields, construction and industrial electrical equipment.
1. Measuring principle of clamp ground resistance meter
The principle of the clamp ground resistance meter is to make full use of "Ohm's law" and must form a measurement circuit with the earth. The jaw is composed of a voltage coil and a current coil. The voltage coil provides an excitation signal and induces an electromotive force E on the measured circuit. Under the action of the potential E, a current 1 will be generated in the measured circuit, and the measured resistance can be obtained by calculating R=E/I.
2. Clamp ground resistance meter measurement method
The clamp ground resistance measurement method is very simple. First press the "ON/OFF" on the panel of the instrument to turn it on, and wait for the 5S instrument to self-check. The standard resistance values are the same, indicating that the clamp ground resistance meter is functioning normally, and then the physical test is carried out.
The physical test only needs to snap the jaws into the ground flat iron or the ground lead, as shown in the figure below: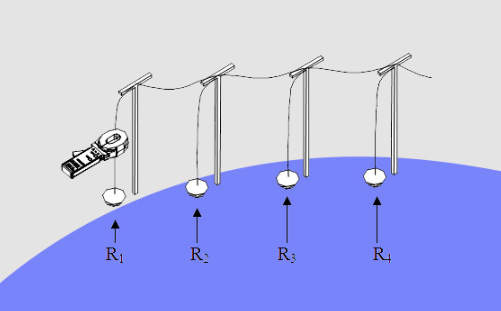
The clamp ground resistance meter is only suitable for multi-point grounding, such as: power transmission system tower grounding, communication cable grounding system, buildings, etc. If there is only one grounding point on site and you want to use multi-point measurement methods, you can use "two Point method", that is, adding an auxiliary grounding point near the independent grounding body, and connecting them together for measurement.




